ERP Software for Small Businesses: A Roadmap to Growth and Success


In the ever-evolving landscape of small businesses, growth and success hinge on adaptability, efficiency, and the ability to make informed decisions. Small business owners often find themselves juggling multiple tasks, managing various aspects of their operations, and facing a myriad of challenges. In such a dynamic environment, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software emerges as a powerful ally, providing a roadmap to growth and success. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the profound impact of ERP software on small businesses, uncovering how it streamlines operations, enhances productivity, and propels these enterprises to new heights.
Before we dive into the transformative potential of ERP software for small businesses, it's essential to understand what ERP software is and how it functions.
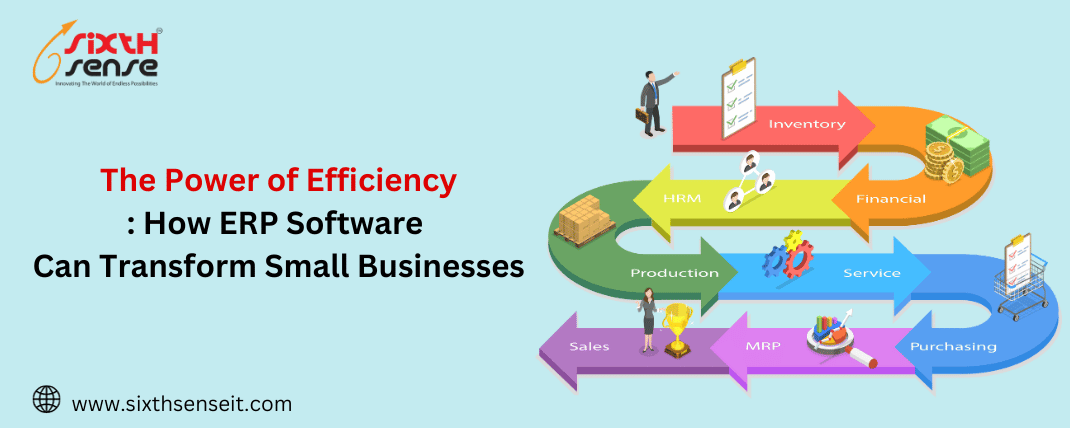
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive suite of integrated applications designed to streamline and automate various business processes within an organization. It acts as a central hub that connects different departments, facilitating real-time data sharing and collaboration. ERP software is engineered to manage and optimize core functions such as:
Finance and Accounting: ERP systems track financial transactions, manage accounts payable and receivable, generate financial reports, and streamline budgeting processes.
Inventory Management: They offer real-time inventory tracking, automate reorder processes, and optimize warehouse management.
Sales and Customer Relationship Management (CRM): ERP software assists in managing customer orders, tracking sales transactions, and improving customer service through CRM tools.
Human Resources: ERP systems maintain employee records, manage payroll and benefits, and streamline recruitment and onboarding processes.
Reporting and Analytics: They provide customizable dashboards, business intelligence tools, and data integration capabilities for in-depth reporting and analytics.
Manufacturing and Production: ERP software helps in defining product structures, scheduling production processes, and ensuring quality control.
Now that we have a clear understanding of what ERP software entails, let's delve into how it can be a catalyst for growth and success for small businesses.
Implementing ERP software offers a plethora of benefits that can reshape the way small businesses operate and significantly contribute to their growth and success. Here are some of the key advantages:
Efficiency is the lifeblood of small businesses. ERP software automates repetitive tasks, streamlines processes, and eliminates manual data entry. This enables your team to allocate their efforts towards strategic activities, resulting in heightened productivity and reduced operational costs.
Small business owners often grapple with the challenge of gaining real-time insights into their operations. ERP systems change that by providing instantaneous access to critical data. You can effortlessly monitor inventory levels, review financial data, track customer orders, and more, all in real time. This visibility empowers you to make informed decisions and respond swiftly to changes in the market.
Manual data entry is susceptible to errors, which can prove costly. ERP software mitigates this risk by automating data entry and validation processes. This ensures that your business records are accurate and dependable, leading to better decision-making and fewer costly mistakes.
Effective communication is essential for any business, but it can be a challenge when different departments work in isolation. ERP systems facilitate seamless communication by offering a centralized platform where team members can access the same data. This minimizes miscommunication and ensures that everyone operates in harmony.
As your small business expands, so do your operational needs. ERP software is designed to scale with your business. You can effortlessly incorporate new features and modules as your business grows, ensuring that your ERP system remains aligned with your expansion.
While implementing an ERP system entails an initial investment, the long-term cost savings can be substantial. By automating processes and reducing manual labor, you can significantly cut operational costs and bolster your bottom line.
Now that we've uncovered the myriad benefits of ERP software, let's shift our focus to the key features to consider when selecting an ERP solution for your small business.
ERP software solutions vary in terms of features and capabilities. To ensure that you choose the right one for your small business, here's a breakdown of key features to consider:
Accounting: Ensure the software offers robust accounting capabilities that enable you to track income and expenses, manage accounts payable and receivable, and generate financial reports.
Budgeting: Look for budgeting tools that assist in creating and monitoring budgets to maintain financial stability.
Payroll: If payroll management is crucial for your business, choose ERP software that provides payroll automation features, including tax calculations and employee payments.
Inventory Tracking: Seek software that provides real-time inventory tracking, allowing you to monitor stock levels, track item movement, and establish automated reorder points.
Warehouse Management: If your business involves warehousing, choose ERP software that optimizes warehouse operations for efficient inventory handling.
Demand Forecasting: Find a solution that offers demand forecasting capabilities, enabling you to predict future inventory needs based on historical data and market trends.
Sales Order Management: Ensure the software can efficiently handle customer orders, track order status, and process sales transactions.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Look for CRM features that allow you to maintain customer records, track interactions, and enhance customer service.
Marketing Automation: If marketing is a key aspect of your business, consider software that helps you create and manage marketing campaigns to attract and retain customers.
Employee Records: Choose ERP software that helps you store and manage employee information, including payroll and benefits data.
Time and Attendance: If you need to track employee work hours and attendance, look for time and attendance tracking features.
Recruitment: Seek software that streamlines the recruitment process, from posting job listings to onboarding new employees, if hiring is a significant part of your business.
Customizable Dashboards: Ensure the software allows you to create personalized dashboards to visualize key performance indicators (KPIs).
Business Intelligence: Look for ERP software that offers robust business intelligence tools, enabling you to generate in-depth reports and analytics to gain insights into your business's performance.
Data Integration: Check whether the ERP system can integrate seamlessly with other data sources to ensure comprehensive reporting.
Bill of Materials (BOM): If your business involves manufacturing, seek software that enables you to define and manage product structures and components.
Work Order Management: Ensure that the ERP software helps you plan and schedule production processes efficiently.
Quality Control: If quality control is crucial for your products, look for features that allow you to monitor product quality and compliance with industry standards.
Now that you have a grasp of the key features to consider, let's move on to the crucial steps involved in selecting the right ERP software for your small business.
Selecting the right ERP software is a pivotal decision that can significantly impact your business's success. To help you make an informed choice, follow these steps:
Commence by conducting a thorough assessment of your specific business needs and challenges. Identify areas where you need the most improvement and determine which ERP features are essential for your operations. Consider factors such as your industry requirements, company size, and growth objectives.
2. Set a Realistic Budget
Establish a budget for your ERP software implementation. Account for both upfront costs (such as software licenses, hardware, and consulting fees) and ongoing expenses (including maintenance, support, and training). Strive to strike a balance between your budget and the anticipated return on investment (ROI).
Research various ERP vendors and solutions available in the market. Take into account factors such as vendor reputation, customer reviews, industry expertise, and the scalability of their software. Create a shortlist of potential vendors that align with your business requirements.
Reach out to the shortlisted vendors to request product demonstrations and free trials. This hands-on experience will enable you to assess the usability and functionality of each ERP system. Involve key stakeholders from your organization in the evaluation process to gather diverse feedback.
Examine whether the ERP software can seamlessly integrate with your existing systems, such as accounting software, e-commerce platforms, and CRM tools. Integration capabilities are critical for maintaining data consistency and achieving a unified view of your business.
Decide whether a cloud-based ERP solution or an on-premises system is a better fit for your needs. Cloud ERP offers scalability, accessibility, and reduced infrastructure costs, while on-premises solutions provide more control over data security and customization.
Evaluate the level of customer support and training provided by the ERP vendor. A robust support system and comprehensive training materials can streamline the implementation process and help your team adapt to the new system more effectively.
8. Plan for Implementation
Once you've chosen an ERP software, create a detailed implementation plan. Define milestones, assign responsibilities, and establish a timeline for the rollout. Consider engaging an experienced ERP consultant or project manager to ensure a smooth implementation.
Now that you've selected the right ERP software for your small business, let's explore the steps involved in implementing it successfully.
The implementation of ERP software is a significant undertaking, but with proper planning and execution, you can minimize disruptions and maximize the benefits. Here's a step-by-step guide to guide you through the implementation process:
Form a dedicated project team that includes key stakeholders, IT professionals, and end-users from various departments. Assign clear roles and responsibilities to team members to ensure effective communication and collaboration.
Before implementing ERP software, meticulously clean and organize your existing data. Ensure that data is accurate, up-to-date, and pertinent to your business processes. Develop a data migration plan to smoothly transfer data from your old systems to the new ERP solution.
Collaborate closely with your ERP vendor to tailor and configure the software to meet your specific business needs. Define workflows, user roles, and permissions to ensure that the system aligns seamlessly with your processes.
Provide comprehensive training to your employees to help them acclimate to the new ERP system. Training should encompass basic navigation, data entry, and department-specific processes. Consider offering ongoing training and support as required.
5. Test the System
Conduct thorough testing to identify and rectify any issues or bugs within the ERP system. Testing should encompass real-world scenarios and involve users from different departments. Address any issues promptly to prevent disruptions during full deployment.
6. Phased Rollout
Contemplate a phased rollout approach to minimize disruptions to your daily operations. Commence with a smaller group of users or specific modules before expanding the implementation to the entire organization. Monitor the system's performance and gather user feedback during this phase.
Following the full implementation of the ERP system, continue to monitor its performance and solicit feedback from users. Identify areas for improvement and fine-tune the system as needed to optimize its functionality.
Implement robust data security measures to safeguard sensitive business information. Regularly back up your data to avert data loss in the event of unforeseen circumstances.
ERP implementation can be intricate, and challenges may arise along the journey. Here are some common challenges and strategies to overcome them:
1. Resistance to Change
Employees may exhibit resistance to adopting new technology and processes. To surmount this challenge, engage employees in the decision-making process, provide training and support, and communicate the benefits of the ERP system.
Data migration can be a complex task, and data quality problems may emerge during the transfer. Prior to migration, meticulously cleanse and validate your data, and devise a contingency plan in case of data-related issues.
Scope creep occurs when the project expands beyond its initial objectives, leading to delays and increased costs. Counter this challenge by defining a clear scope for your ERP implementation and adhering to it. Carefully assess and document any requested changes.
Inadequate training can result in user frustration and errors. Invest in comprehensive training programs and provide ongoing support to help users become proficient with the new system.
Without the backing of senior management, ERP implementation may encounter roadblocks. Garner support from top executives by demonstrating the potential ROI and strategic advantages of the ERP system.
Implementing ERP software represents a significant investment, both in terms of time and financial resources. To maximize the return on your investment, consider the following strategies:
Regularly assess the performance of your ERP system and seek opportunities to further optimize processes. As your business evolves, your ERP software should adapt to your evolving needs.
Leverage the analytics and reporting capabilities of your ERP system to gain profound insights into your business operations. Identify trends, analyze customer behavior, and make data-driven decisions to drive growth.
Keep your ERP software up-to-date by applying the latest updates and patches provided by the vendor. This ensures that your system remains secure and compatible with evolving technologies.
Promote collaboration among your team members by utilizing the communication features of your ERP system. Enhanced collaboration can lead to more effective problem-solving and innovation.
As your business expands and diversifies, consider expanding your ERP system with additional modules and features. Explore opportunities to integrate new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to further enhance efficiency and competitiveness.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software serves as an indispensable tool in the arsenal of small businesses striving for growth and success. By centralizing and automating core business processes, ERP software delivers enhanced efficiency, real-time visibility, and sustained growth. Nevertheless, the path to successful ERP implementation requires meticulous planning, unwavering teamwork, and continuous refinement.
When selecting an ERP solution, assess your business's unique needs, evaluate integration capabilities, and scrutinize vendor support and training options. During implementation, prioritize data quality, user training, and phased rollout to minimize disruptions. Be prepared to tackle common challenges and secure executive support to ensure a seamless transition.
In the end, while the investment in ERP software represents a considerable commitment, it also offers substantial returns. It empowers your small business to operate more efficiently, make data-driven decisions, and adapt to the ever-changing business landscape. With the right ERP system in place, you can chart a course for long-term success, resilience, and prosperity in the dynamic world of small business.