Streamline Your Small Business Operations with ERP Software: A Comprehensive Guide

In the fast-paced world of small business, efficiency is key to success. As a small business owner, you wear many hats and juggle numerous tasks daily. Keeping track of finances, managing inventory, handling customer orders, and coordinating with your team can be overwhelming. This is where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software comes to your rescue. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore how ERP software can streamline your small business operations, boost productivity, and help you thrive in today's competitive market.
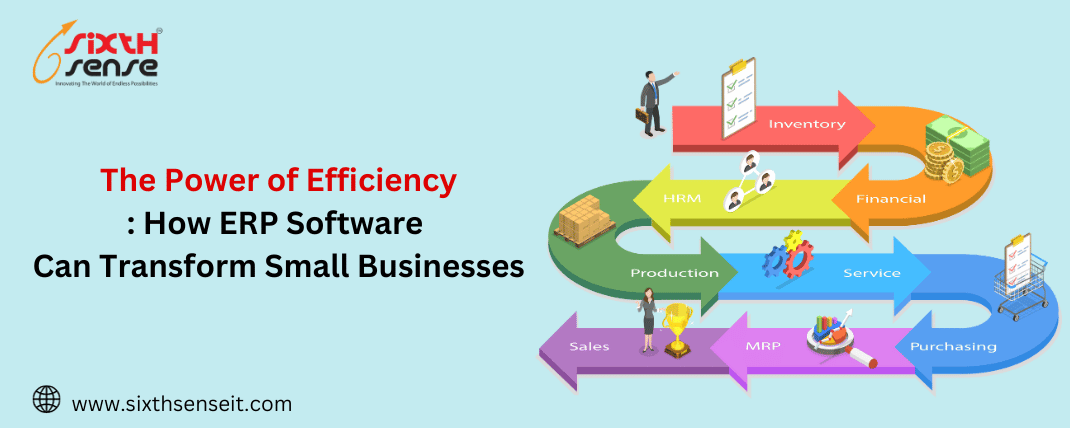
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a powerful tool that integrates various business processes into a single, unified system. It provides a centralized platform for managing and automating core functions such as finance, human resources, inventory management, sales, and customer relationship management (CRM). ERP software enables real-time data sharing and collaboration among different departments within your organization, allowing you to make informed decisions and optimize your operations.
Implementing ERP software can bring a multitude of benefits to your small business. Here are some of the key advantages:
One of the primary benefits of ERP software is improved efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining processes, your team can focus on more strategic activities, which can ultimately lead to higher productivity and reduced operational costs.
ERP systems provide real-time visibility into your business operations. You can access up-to-date information about inventory levels, financial data, customer orders, and more with just a few clicks. This visibility enables better decision-making and allows you to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
Manual data entry is prone to errors, which can result in costly mistakes. ERP software reduces the risk of errors by automating data entry and validation processes. This ensures that your business records are accurate and reliable.
ERP systems facilitate seamless communication within your organization. Team members can access the same data and collaborate more effectively. This reduces miscommunication and ensures that everyone is on the same page.
As your small business grows, ERP software can easily scale to accommodate your changing needs. You can add new features and modules as your business expands, ensuring that your ERP system continues to support your growth.
While implementing an ERP system may require an initial investment, the long-term cost savings can be substantial. By automating processes and reducing manual labor, you can lower operational costs and increase your bottom line.
ERP software offers a wide range of features designed to streamline various aspects of your business. Here are some key features to look for when choosing an ERP solution:
Accounting: Track income and expenses, manage accounts payable and receivable, and generate financial reports.
Budgeting: Create and monitor budgets to ensure financial stability.
Payroll: Automate payroll processes, including tax calculations and employee payments.
Inventory Tracking: Monitor stock levels, track item movement, and set up automated reorder points.
Warehouse Management: Optimize warehouse operations for efficient inventory handling.
Demand Forecasting: Predict future inventory needs based on historical data and market trends.
Sales Order Management: Manage customer orders, track order status, and process sales transactions.
Customer Relationship Management: Maintain customer records, track interactions, and improve customer service.
Marketing Automation: Create and manage marketing campaigns to attract and retain customers.
Employee Records: Store and manage employee information, including payroll and benefits data.
Time and Attendance: Track employee work hours and attendance.
Recruitment: Streamline the hiring process, from posting job listings to onboarding new employees.
Customizable Dashboards: Create personalized dashboards to visualize key performance indicators (KPIs).
Business Intelligence: Generate in-depth reports and analytics to gain insights into your business's performance.
Data Integration: Connect your ERP system with other data sources for comprehensive reporting.
Bill of Materials (BOM): Define and manage product structures and components.
Work Order Management: Plan and schedule production processes efficiently.
Quality Control: Monitor product quality and compliance with industry standards.
Selecting the right ERP software is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business's success. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed choice:
Start by evaluating your specific business needs and challenges. Identify the areas where you need the most improvement and determine which features are essential for your operations. Consider factors such as industry requirements, company size, and growth goals.
Establish a budget for your ERP software implementation. Be sure to account for both upfront costs (software licenses, hardware, and consulting fees) and ongoing expenses (maintenance, support, and training). It's essential to balance your budget with your expected return on investment (ROI).
Research different ERP vendors and solutions available in the market. Consider factors such as vendor reputation, customer reviews, industry expertise, and the scalability of their software. Create a shortlist of potential vendors that align with your business requirements.
Contact the shortlisted vendors to request product demonstrations and free trials. This hands-on experience will help you assess the usability and functionality of each ERP system. Involve key stakeholders from your organization in the evaluation process to gather diverse feedback.
Check whether the ERP software can seamlessly integrate with your existing systems, such as accounting software, e-commerce platforms, and CRM tools. Integration capabilities are crucial for data consistency and a unified view of your business.
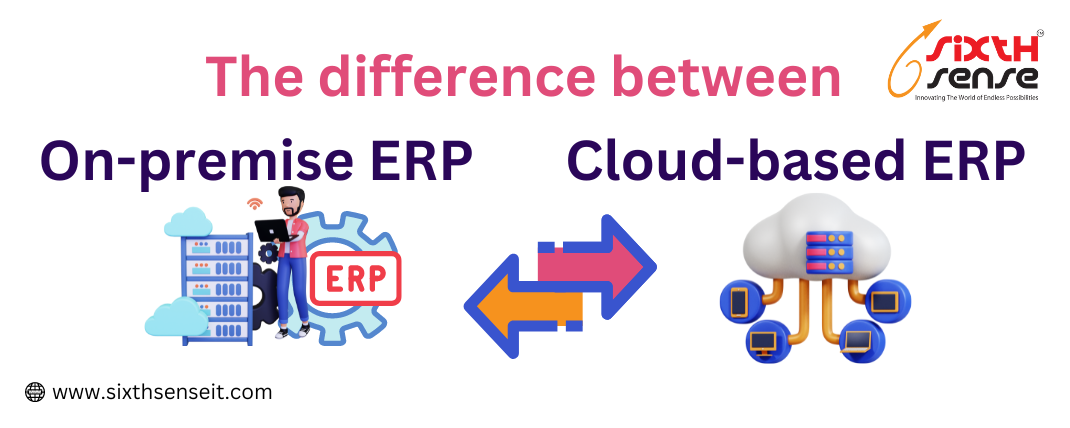
Decide whether you want to opt for a cloud-based ERP solution or an on-premises system. Cloud ERP offers scalability, accessibility, and reduced infrastructure costs, while on-premises solutions provide more control over data security and customization.
Evaluate the level of customer support and training provided by the ERP vendor. A robust support system and comprehensive training materials can make the implementation process smoother and help your team adapt to the new system more quickly.
Once you've chosen an ERP software, create a detailed implementation plan. Define milestones, assign responsibilities, and establish a timeline for the rollout. Consider involving an experienced ERP consultant or project manager to ensure a successful implementation.
Implementing ERP software is a significant undertaking, but with proper planning and execution, you can minimize disruptions and maximize the benefits. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you through the implementation process:
Form a dedicated project team that includes key stakeholders, IT professionals, and end-users from various departments. Assign clear roles and responsibilities to team members to ensure effective communication and collaboration.
Before implementing ERP software, clean and organize your existing data. Ensure that data is accurate, up-to-date, and relevant. Develop a data migration plan to transfer data from your old systems to the new ERP solution.
Work closely with your ERP vendor to customize and configure the software to meet your specific business needs. Define workflows, user roles, and permissions to ensure that the system aligns with your processes.
Provide comprehensive training to your employees to help them adapt to the new ERP system. Training should cover basic navigation, data entry, and specific processes related to each department. Consider offering ongoing training and support as needed.
Conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve any issues or bugs in the ERP system. Testing should include real-world scenarios and involve users from different departments. Address any issues promptly to avoid disruptions during full deployment.
Consider a phased rollout approach to minimize disruptions to your daily operations. Start with a smaller group of users or specific modules before expanding to the entire organization. Monitor the system's performance and gather user feedback during this phase.
After the ERP system is fully implemented, continue to monitor its performance and gather feedback from users. Identify areas for improvement and fine-tune the system as needed to optimize its functionality.
Implement robust data security measures to protect sensitive business information. Regularly back up your data to prevent data loss in case of unforeseen events.
ERP implementation can be complex, and challenges may arise along the way. Here are some common challenges and tips on how to overcome them
Employees may resist adopting new technology and processes. To overcome this challenge, involve employees in the decision-making process, provide training and support, and communicate the benefits of the ERP system.
Data migration can be tricky, and data quality problems can occur during the transfer. Thoroughly clean and validate data before migration, and have a backup plan in case of data-related issues.
Scope creep happens when the project expands beyond its initial objectives, leading to delays and increased costs. Define a clear scope for your ERP implementation and stick to it. Carefully evaluate and document any requested changes.
Inadequate training can lead to user frustration and errors. Invest in comprehensive training programs and provide ongoing support to help users become proficient with the new system.
Without the support of senior management, ERP implementation can face roadblocks. Secure buy-in from top executives by demonstrating the potential ROI and strategic benefits of the ERP system.
Implementing ERP software is a significant investment, both in terms of time and money. To maximize the return on your investment, consider the following strategies:
Regularly assess the performance of your ERP system and look for opportunities to optimize processes further. As your business evolves, your ERP software should adapt to your changing needs
Use the analytics and reporting capabilities of your ERP system to gain insights into your business operations. Identify trends, analyze customer behavior, and make data-driven decisions to drive growth.
Keep your ERP software up-to-date with the latest updates and patches provided by the vendor. This ensures that your system remains secure and compatible with evolving technologies.
Encourage collaboration among your team members by leveraging the communication features of your ERP system. Improved collaboration can lead to better problem-solving and innovation.
As your business grows, consider expanding your ERP system with additional modules and features. Explore opportunities to integrate new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to further enhance efficiency.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a game-changer for small businesses looking to streamline their operations and compete effectively in today's dynamic market. By centralizing and automating core business processes, ERP software can improve efficiency, enhance visibility, and drive growth. However, successful ERP implementation requires careful planning, dedicated teamwork, and ongoing optimization.
When selecting an ERP solution, evaluate your business needs, consider integration capabilities, and assess the vendor's support and training options. During implementation, focus on data quality, user training, and phased rollout to minimize disruptions. Be prepared to address common challenges and ensure executive support for a smooth transition.
In the end, the investment in ERP software can yield substantial returns by enabling your small business to operate more efficiently, make data-driven decisions, and adapt to changing market conditions. With the right ERP system in place, you can position your small business for long-term success in a competitive business landscape.