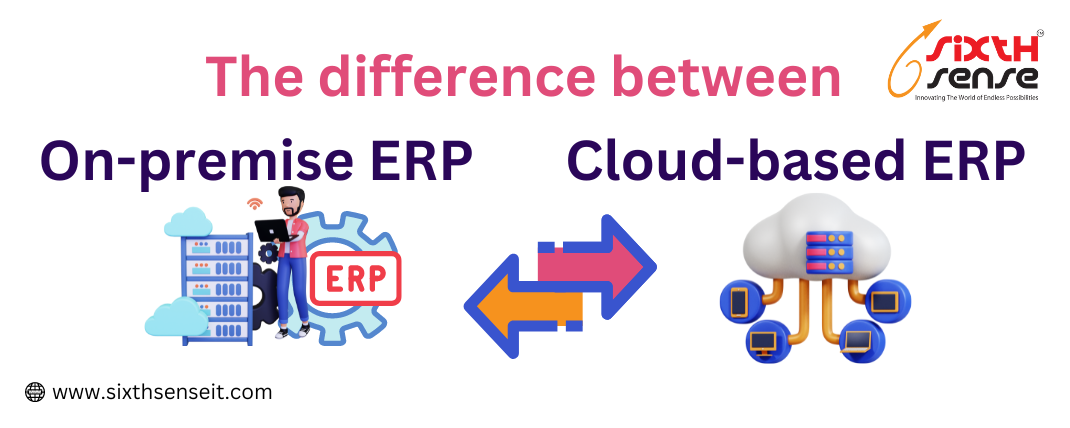
The benefits of cloud computing for your business


Cloud computing is a model of delivering computing resources and services over the internet, rather than owning and maintaining physical hardware and infrastructure. With cloud computing, organizations can access computing resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, as a service on an as-needed basis.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model in which a third-party provider delivers infrastructure resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. With IaaS, organizations can access these resources on demand, rather than having to invest in and maintain their own physical infrastructure.
IaaS allows organizations to outsource the infrastructure management and maintenance to the provider, freeing up their time and resources to focus on their core business. IaaS can be particularly beneficial for small businesses that may not have the budget or expertise to manage their own infrastructure.
IaaS providers typically offer a range of options for computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking, which can be customized to meet the needs of the organization. IaaS providers also offer various pricing models, such as pay-per-use, subscription-based, and reserved instances, allowing organizations to choose the model that best fits their needs.
Some examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model in which a third-party provider delivers a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications over the internet. With PaaS, organizations can access a complete development environment without having to maintain the underlying infrastructure.
PaaS allows organizations to focus on developing and deploying their applications, rather than worrying about the infrastructure and maintenance required to support them. This can be particularly useful for small businesses that may not have the resources or expertise to manage their own infrastructure.
PaaS providers typically offer a range of tools and services, such as development frameworks, databases, and middleware, which can be used to build and deploy applications. PaaS providers also offer various pricing models, such as pay-per-use, subscription-based, and reserved instances, allowing organizations to choose the model that best fits their needs.
Some examples of PaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing model in which a third-party provider delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. With SaaS, organizations can use software applications without having to purchase and install them on their own servers.
SaaS allows organizations to access software applications on demand, rather than having to invest in the hardware and infrastructure required to support them. This can be particularly useful for small businesses that may not have the resources or expertise to manage their own infrastructure.
SaaS providers typically offer a range of software applications, such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and productivity tools. SaaS providers also offer various pricing models, such as pay-per-use, subscription-based, and volume-based, allowing organizations to choose the model that best fits their needs.
Some examples of SaaS providers include Miss CRM, Microsoft Office 365, and Adobe Creative Cloud.
Cloud computing has become an essential part of many businesses' IT strategies, and it's easy to see why. With its numerous benefits, it's no wonder that so many organizations are making the switch to the cloud.
One of the main benefits of cloud computing is the cost savings it can provide. With a pay-as-you-go model, you only pay for the resources you use, rather than having to invest in and maintain expensive physical hardware. This can significantly reduce your IT infrastructure costs. Additionally, with cloud computing, you can take advantage of economies of scale, as you're able to share resources with other organizations. This can further reduce your costs and increase your efficiency.
Cloud computing allows you to easily scale up or down your resources based on your needs. If your business experiences a sudden increase in demand, you can quickly and easily increase your capacity to meet the demand. Conversely, if you experience a decrease in demand, you can scale down your resources to save costs. This flexibility can help you optimize your costs and avoid over-provisioning or under-provisioning of resources.
Cloud computing enables you to access your data and applications from any device, at any time and from anywhere, giving you greater flexibility to work when and where you need to. This can be particularly useful for businesses with remote workers or those that operate in multiple locations. With cloud computing, you're not limited to a single location or device, and you can work from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud computing provides built-in disaster recovery and backup capabilities, which can help protect your data and reduce downtime in the event of a disaster. This can be especially important for businesses that rely on their IT systems to operate. With cloud computing, you don't have to worry about the risk of data loss or downtime due to hardware failure, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events.
Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures to protect your data, and often have more advanced security protocols in place than many businesses can afford to implement on their own. This can give you peace of mind knowing that your data is secure and compliant. Additionally, with cloud computing, you don't have to worry about the cost and complexity of managing your own security infrastructure.
Cloud computing allows team members to easily collaborate on projects and share documents in real-time, regardless of their location. This can improve communication and productivity within your organization. With cloud computing, you don't have to worry about the challenges of coordinating work between different locations or devices.
By using cloud computing, businesses can take advantage of the latest technology and innovation without having to invest in new hardware and infrastructure. This can help you stay competitive and ahead of the curve. With cloud computing, you can easily access the latest tools and technologies, without having to worry about the cost and complexity of implementing them in-house.
In conclusion, cloud computing can provide a number of benefits for businesses of all sizes. From cost savings and scalability to flexibility and security, the advantages of using the cloud are numerous. If you're considering moving your business to the cloud, it's worth considering the many benefits it can offer. With its cost savings, scalability, flexibility, disaster recovery, security, collaboration, and innovation, cloud computing can help your business operate more efficiently, stay competitive, and drive growth. So, it's definitely worth considering for your business.